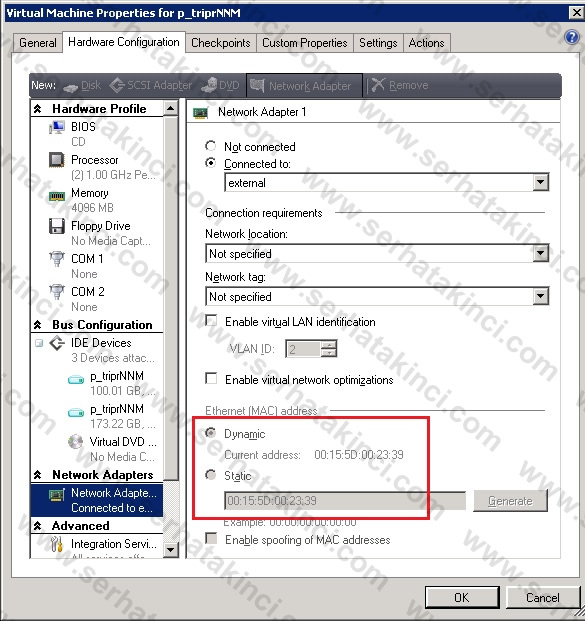
In most network deployments, generated MAC addresses are appropriate. However, you might need to set a static MAC address for a virtual network adapter. The following examples show when you might set a static MAC address. The dynamic MAC addresses it generates, however, depend on the first dynamic IP address it took from the DHCP Server. This means that if we add another Hyper-V host to the infrastructure and it gets the same IP 10.10.10.10 from the DHCP Server that had the first host, then the dynamic MAC addresses it generates will be the same as the first host.
-->Applies to: Windows Server 2016
When you configure a NIC Team with switch independent mode and either address hash or dynamic load distribution, the team uses the media access control (MAC) address of the primary NIC Team member on outbound traffic. The primary NIC Team member is a network adapter selected by the operating system from the initial set of team members. It is the first team member to bind to the team after you create it or after the host computer is restarted. Because the primary team member might change in a non-deterministic manner at each boot, NIC disable/enable action, or other reconfiguration activities, the primary team member might change, and the MAC address of the team might vary.
In most situations this doesn't cause problems, but there are a few cases where issues might arise.
Mac Address Lookup
If the primary team member is removed from the team and then placed into operation there may be a MAC address conflict. To resolve this conflict, disable and then enable the team interface. The process of disabling and then enabling the team interface causes the interface to select a new MAC address from the remaining team members, thereby eliminating the MAC address conflict.
You can set the MAC address of the NIC team to a specific MAC address by setting it in the primary team interface, just as you can do when configuring the MAC address of any physical NIC.
MAC address use on transmitted packets
When you configure a NIC Team in switch independent mode and either address hash or dynamic load distribution, the packets from a single source (such as a single VM) is simultaneously distributed across multiple team members. To prevent the switches from getting confused and to prevent MAC flapping alarms, the source MAC address is replaced with a different MAC address on the frames transmitted on team members other than the primary team member. Because of this, each team member uses a different MAC address, and MAC address conflicts are prevented unless and until failure occurs.
When a failure is detected on the primary NIC, the NIC Teaming software starts using the primary team member's MAC address on the team member that is chosen to serve as the temporary primary team member (i.e., the one that will now appear to the switch as the primary team member). This change only applies to traffic that was going to be sent on the primary team member with the primary team member's MAC address as its source MAC address. Other traffic continues to be sent with whatever source MAC address it would have used prior to the failure.
Mac Address Example

Following are lists that describe NIC Teaming MAC address replacement behavior, based on how the team is configured:
In Switch Independent mode with Address Hash distribution
All ARP and NS packets are sent on the primary team member
All traffic sent on NICs other than the primary team member are sent with the source MAC address modified to match the NIC on which they are sent
All traffic sent on the primary team member is sent with the original source MAC address (which may be the team's source MAC address)
In Switch Independent mode with Hyper-V Port distribution
Every vmSwitch port is affinitized to a team member
Every packet is sent on the team member to which the port is affinitized
No source MAC replacement is done
In Switch Independent mode with Dynamic distribution
Every vmSwitch port is affinitized to a team member
All ARP/NS packets are sent on the team member to which the port is affinitized
Packets sent on the team member that is the affinitized team member have no source MAC address replacement done
Packets sent on a team member other than the affinitized team member will have source MAC address replacement done
In Switch Dependent mode (all distributions)
- No source MAC address replacement is performed
Related topics
Manual Dynamic Mac Address Table
NIC Teaming: In this topic, we give you an overview of Network Interface Card (NIC) Teaming in Windows Server 2016. NIC Teaming allows you to group between one and 32 physical Ethernet network adapters into one or more software-based virtual network adapters. These virtual network adapters provide fast performance and fault tolerance in the event of a network adapter failure.
NIC Teaming settings: In this topic, we give you an overview of the NIC Team properties such as teaming and load balancing modes. We also give you details about the Standby adapter setting and the Primary team interface property. If you have at least two network adapters in a NIC Team, you do not need to designate a Standby adapter for fault tolerance.
Create a new NIC Team on a host computer or VM: In this topic, you create a new NIC Team on a host computer or in a Hyper-V virtual machine (VM) running Windows Server 2016.
Troubleshooting NIC Teaming: In this topic, we discuss ways to troubleshoot NIC Teaming, such as hardware, physical switch securities, and disabling or enabling network adapters using Windows PowerShell.